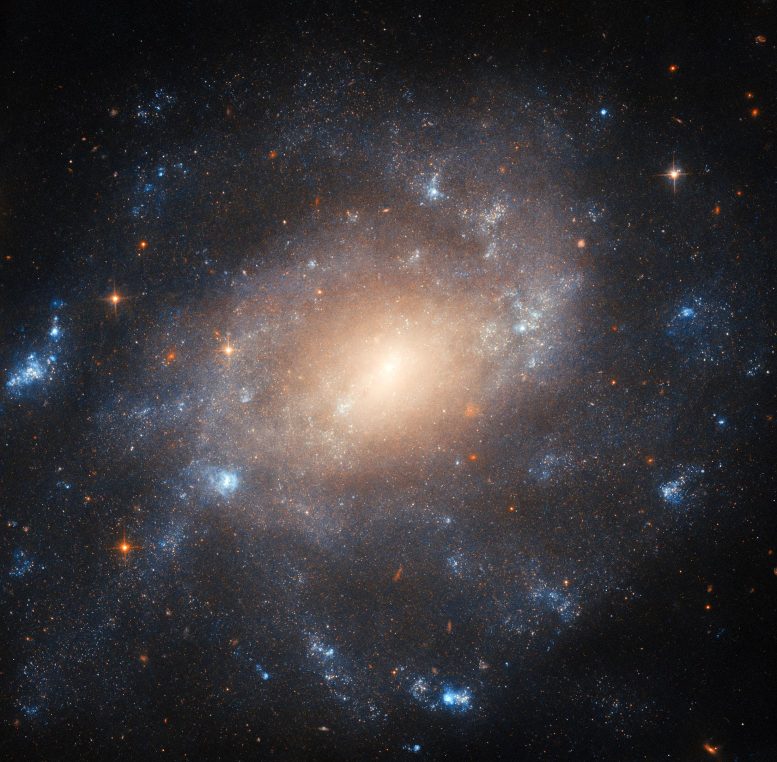

This Hubble Space Telescope image captures the spiral galaxy ESO 422-41 in the constellation Columba, showcasing its detailed spiral arms and luminous core. The image is part of a long tradition of astronomical observations, tracing back to the era of large photographic surveys in the 1970s. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, C. Kilpatrick
Hubble’s detailed image of the spiral galaxy ESO 422-41 highlights both its star-filled structure and historical significance in astronomical surveys.
This Hubble Picture of the Week depicts the spiral galaxy ESO 422-41, which is located approximately 34 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Columba. The patchy, star-filled structure of the galaxy’s spiral arms and the glow from its dense core are laid out in intricate detail here by Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys. Images of this galaxy have, however, a decades-long history.
Historical Context of Astronomical Observations
The name ESO 422-41 comes from its identification in the European Southern Observatory (B) Atlas of the Southern Sky. In the times before automated sky surveys with space observatories such as ESA’s Gaia, many stars, galaxies, and nebulae were discovered by means of large photographic surveys.
Astronomers used the most advanced large telescopes of the time to produce hundreds of photographs, covering an area of the sky. They later studied the resulting photographs, attempting to catalog all the new astronomical objects revealed.
Advances in Astronomical Techniques
In the 1970s a new telescope at ESO’s La Silla facility in Chile performed such a survey of the southern sky, which still had not been examined in as much depth as the sky in the north. At the time, the premier technology for recording images was glass plates treated with chemicals. The resulting collection of photographic plates became the ESO (B) Atlas of the Southern Sky.
Astronomers at ESO and in Uppsala, Sweden collaborated to study the plates, recording hundreds of galaxies — ESO 422-41 being just one of those — star clusters, and nebulae. Many were new to astronomy.
Evolution of Sky Surveying
Astronomical sky surveying has since transitioned through digital, computer-aided surveys such as the Sloan Digital Sky Survey and the Legacy Surveys, to surveys made by space telescopes including Gaia and the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer.
Even so, photographic sky surveys contributed immensely to astronomical knowledge for decades, and the archives of glass plates serve as an important historical reference for large swathes of the sky. Some are still actively used today, for instance, to study variable stars through time. And the objects that these surveys revealed, including ESO 422-41, can now be studied in depth by telescopes such as Hubble.








How is it that Hubble can capture detailed images of solar systems and galaxies millions, and even tens to hundreds of millions, of light years away; yet cannot give us images of the moon landing sites because they are “too small”?