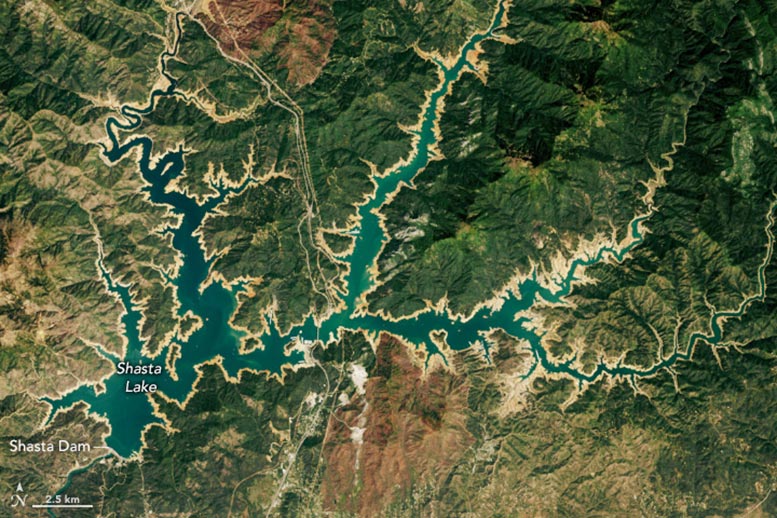

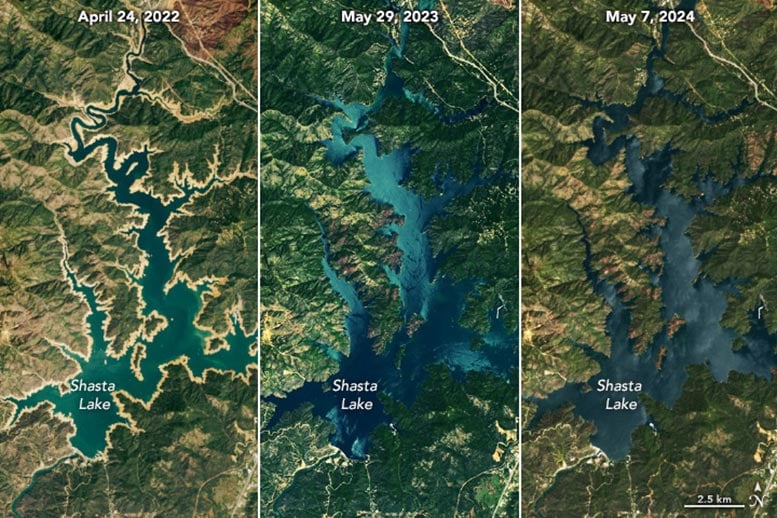
Satellite image of Shasta Lake captured on April 24, 2022, by the Operational Land Imager-2 on Landsat 9.
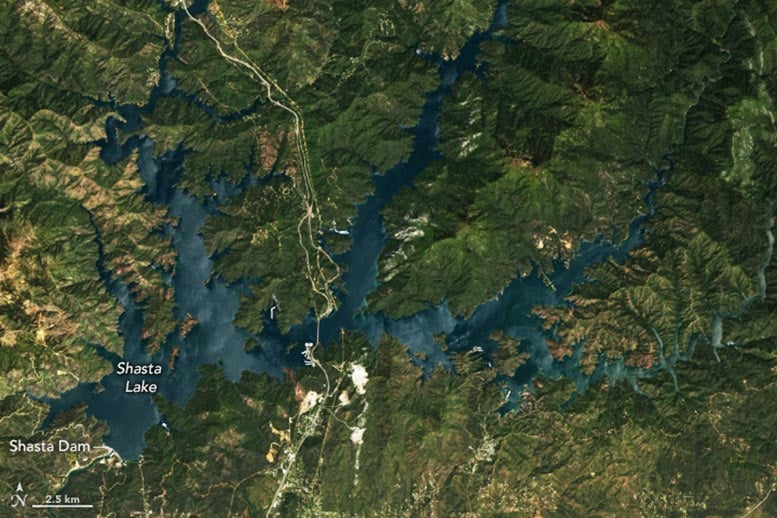
Satellite image of Shasta Lake captured on May 7, 2024, by the Operational Land Imager on Landsat 8.
For the second year in a row, California’s largest reservoir filled to nearly 100 percent capacity.
Following consecutive wet winters, Shasta Lake in Northern California reached full capacity for the second year in a row, in time for summer 2024. As the state’s largest reservoir, crucial for irrigation, municipal water supplies, flood control, and more, it also neared 100 percent capacity in the spring 2023. The healthy cache of water in back-to-back years marked a significant recovery from the drought and low water levels experienced from 2019 to 2022.
On May 7, 2024, the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on the Landsat 8 satellite captured the above image (lower) of Shasta Lake, showing it at 96 percent of its total capacity, which is 114 percent of the average for that date. In contrast, the image above (upper) taken by Landsat 9 on April 24, 2022, showed the lake at only 39 percent capacity. That May, the reservoir topped out for the year at a mere 40 percent of its total capacity.
A prolonged period of extreme drought, starting in 2019, left reservoir levels low for several years. But in the early months of 2023, heavy rains and meltwater from an above-average mountain snowpack initiated a remarkable rebound. By May 29 of that year, the lake had filled to 98 percent of capacity. The tan fringe, or “bathtub ring,” around its perimeter that was visible in 2022 had vanished.
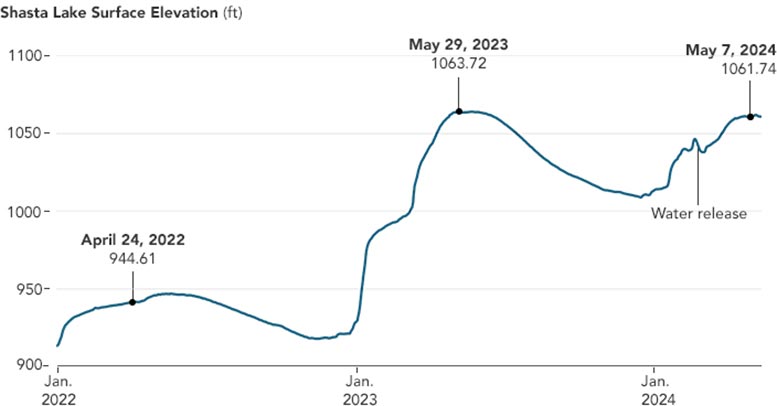
In 2024, Shasta Lake water levels again began rising quickly in mid-January as moisture-laden storms passed through the region. But as this chart shows, lake elevations at the start of the year were much higher in 2024 than in 2023. By mid-February 2024, officials deemed the reservoir “too high” for that time of year, according to news reports. The U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, which manages the dam, temporarily increased water releases to as much as seven times the winter baseline rate to create space for water from future storms and to minimize flood risk downstream. It was the first time since 2019 that managers had to conduct this sort of flood control.
The early 2024 rainfall was a boon to other water supplies in California. Lake Oroville, the state’s second-largest reservoir, also reached full capacity for the second year in a row. Even with controlled water releases throughout the winter, the reservoir held 128 percent of its average capacity in early May 2024.
Surface water is but one part of the picture in California. Groundwater makes up 40 percent of the state’s water supply in typical years and can contribute up to 60 percent in dry ones. According to a recent report from the California Department of Water Resources, managed groundwater recharge added 4.1 million acre-feet—almost one full Shasta Lake’s worth of water—to underground reservoirs in the last water year (October 2022 through September 2023). This was the first yearly gain in groundwater stores recorded since 2019. However, the agency estimates it would take five consecutive above-average water years to make up for the deficit incurred over the past two decades.
NASA Earth Observatory images by Wanmei Liang, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey and surface elevation data from California Department of Water Resources.









Be the first to comment on "From Drought to Drenched: Stunning Rebound of California’s Largest Reservoir"