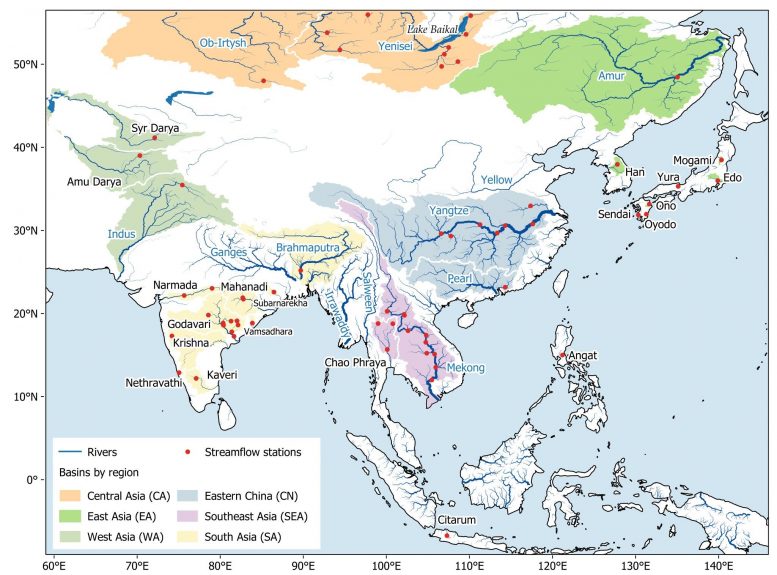
Figure 1. Map of the Asian Monsoon region; river basins involved in this study are highlighted by subregion, rivers belonging to the world’s 30 biggest are shown with names indicated in blue. Credit: SUTD
The Singapore University of Technology and Design study will be crucial for assessing future climatic changes and making more informed water management decisions.
813 years of annual river discharge at 62 stations, 41 rivers in 16 countries, from 1200 to 2012. That is the data that researchers at the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) produced after two years of research in order to better understand past climate patterns of the Asian Monsoon region.
Home to many populous river basins, including ten of the world’s biggest rivers (Figure 1), the Asian Monsoon region provides water, energy, and food for more than three billion people. This makes it crucial for us to understand past climate patterns so that we can better predict long term changes in the water cycle and the impact they will have on the water supply.
To reconstruct histories of river discharge, the researchers relied on tree rings. An earlier study by Cook et al. (2010) developed an extensive network of tree ring data sites in Asia and created a paleodrought record called the Monsoon Asia Drought Atlas (MADA). SUTD researchers used the MADA as an input for their river discharge model. They developed an innovative procedure to select the most relevant subset of the MADA for each river based on hydroclimatic similarity. This procedure allowed the model to extract the most important climate signals that influence river discharge from the underlying tree ring data.
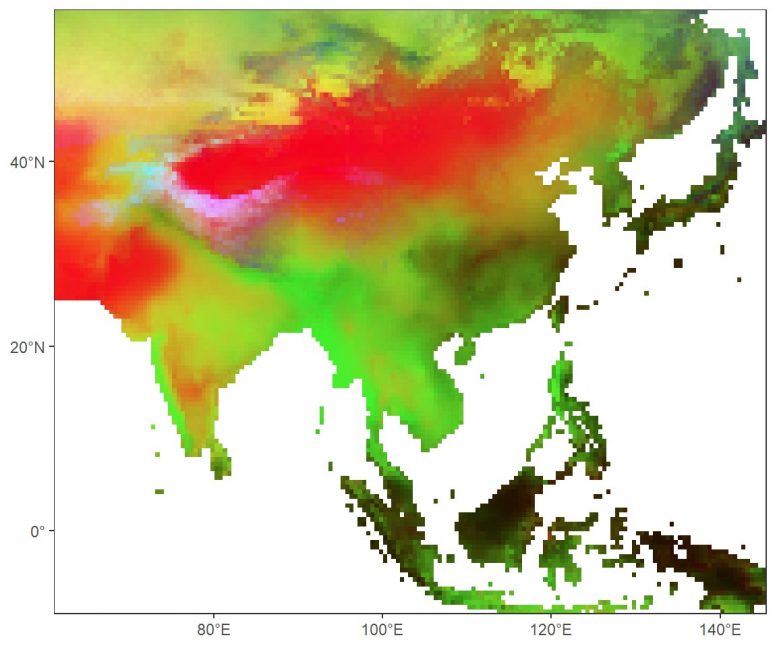
Figure 2. This “heat map” shows the reconstructed history of 62 river reaches (each row) over 812 years (each column). The stations are arranged approximately north to south (top down on y‐axis) and divided into five regions as delineated in Figure 1: CA (Central Asia), EA (East Asia), WA (West Asia), CN (eastern China), SEA (Southeast Asia), and SA (South Asia). Credit: SUTD
“Our results reveal that rivers in Asia behave in a coherent pattern. Large droughts and major pluvial periods have often occurred simultaneously in adjacent or nearby basins. Sometimes, droughts stretched as far as from the Godavari in India to the Mekong in Southeast Asia (Figure 2). This has important implications for water management, especially when a country’s economy depends on multiple river basins, like in the case of Thailand,” explained first author Nguyen Tan Thai Hung, a PhD student from SUTD.
DOI: 10.1029/2020WR027883Acknowledgment: Hung Nguyen is supported by the President’s Graduate Fellowship from the Singapore University of Technology and Design. We thank Edward Cook, Caroline Ummenhofer, Nerilie Abram, Nathalie Goodkin, Xun Sun, Murray Peel, Rory Nathan, and Robert Wasson for their insightful comments. We are indebted to Michelle Ho, Justin Maxwell, Valerie Trouet, two anonymous reviewers, and the Associate Editor for their constructive reviews. We are grateful to Thanh Dang, Mukund Rao, Christoph Libisch‐Lehner, Rosanne D’Arrigo, Donghoon Lee, and Caroline Leland for streamflow data of the Mekong, Brahmaputra, Angat, Citarum, Han, and Yeruu Rivers.









Be the first to comment on "800 Years of Paleoclimate Patterns Unearthed in Largest Study of Asia’s Rivers"