A research team has developed an advanced aqueous zinc-ion battery with an enhanced cycle lifespan using a weak magnetic field and a new VS2 material. The breakthrough addresses the challenges of zinc dendrite growth and cathode material limitations. Credit: Mao Yunjie
A research team at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), led by Prof. Zhao Bangchuan, developed a high-performance aqueous zinc-ion battery with ultralong cycle lifespan in a weak magnetic field.
The findings were recently published in the journal Materials Horizons.
Aqueous zinc-ion batteries are a low-cost and safe alternative to lithium-ion batteries with high theoretical capacity. However, the limited electrochemical performance of cathode material and zinc dendrite growth on the anode reduces the energy density and cycle life of an aqueous zinc-ion battery. To develop better aqueous zinc-ion batteries, it’s important to design high-energy-density cathodes and suppress zinc dendrite growth.
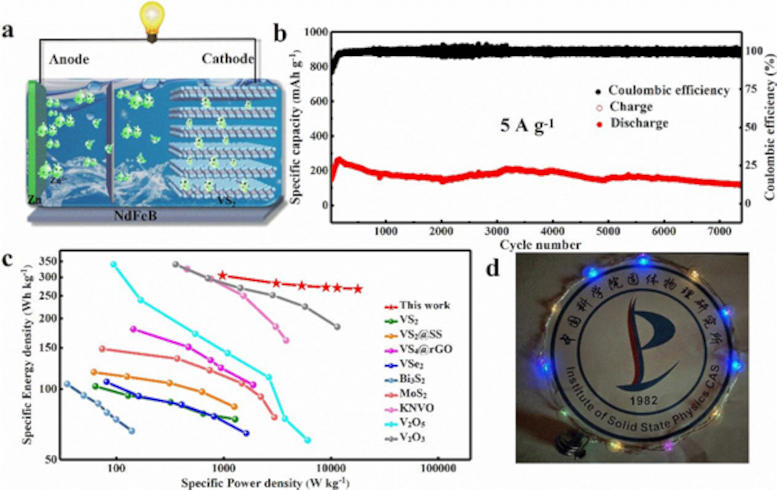
Schematic illustration and electrochemical performance of the Zn-VS2 AZIB. (a) Schematic illustration of the Zn-VS2 AZIB configuration.(b) Ultralong cycle performance of the vacancy-rich Zn-VS 2 AZIB. (c) Ragone plots of the vacancy-rich VS2 compared with the other cathodes. (d) Opticalphoto of an LED lamp powered by the Zn-VS2 batteries. Credit: Mao Yunjie
In this research, the team overcame the limitations of existing cathode materials and the issue of zinc dendrite growth. They used a one-step hydrothermal method with in-situ electrochemical defect engineering to create a VS2 material. This material had rich defects that were effective in reducing the electrostatic interaction between zinc ions and VS2. It allowed for 3D transport of Zn2+ along both the ab plane and c-axis, resulting in excellent rate capability.
While cycling stability remained an issue due to the dendrite growth, the team found that introducing an external magnetic field suppressed the growth and significantly enhanced the battery’s lifespan. Operating under a weak magnetic field, the high-performance Zn-VS2 battery demonstrated an ultralong cycle lifespan and delivered a high energy density and power density.
The work could have significant implications for the future of energy storage technology, according to the team.
Reference: “Magneto-electrochemistry driven ultralong-life Zn-VS2 aqueous zinc-ion batteries” by Yunjie Mao, Jin Bai, Jianguo Si, Hongyang Ma, Wanyun Li, Peiyao Wang, Hongli Zhang, Zhigao Sheng, Xiaoguang Zhu, Peng Tong, Xuebin Zhu, Bangchuan Zhao and Yuping Sun, 19 May 2023, Materials Horizons.
DOI: 10.1039/D3MH00303E








EOS Energy is already producing modular, containerized aqueous zinc batteries for commercial & micro grid applications in Pittsburgh PA.