
From left are Junyoung Kim, Professor Guntae Kim, and Ohhun Gwona in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST.
A joint research team, affiliated with UNIST has introduced the Hybrid-Solid Electrolysis Cell (Hybrid-SOEC) system with the highest reported electrochemical performance in hydrogen production. The proposed system has attracted much attention as a new promising option for cost-effective and highly-efficient hydrogen production, as it shows excellent performance compared with other water-electrolysis systems.
This breakthrough has been led by Professor Guntae Kim in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST in collaboration with Professor Tak-Hyoung Lim of Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) and Professor Jeeyoung Shin of Sookmyung Women’s University.
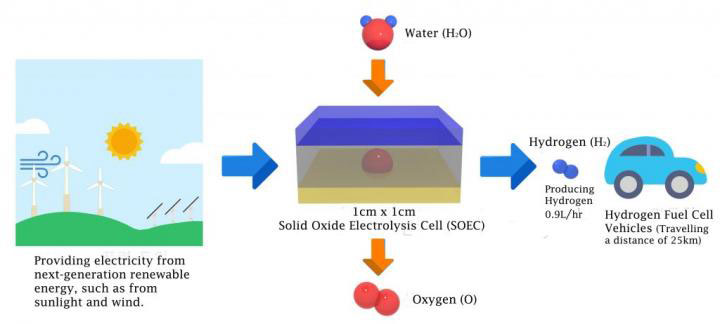
A solid oxide electrolyzer cell (SOEC) consists of two electrodes and an electrolyte that are all in solid state. They are strongly desired as novel candidates for hydrogen production, as they require no need to replenish lost electrolytes, while eliminating corrosion problems. Besides, SOECs also operate at relatively high temperatures (700-1000 °C or 1,300-1,800 °F), which helps to offer reduced electrical energy consumption.
The economic impact of SOEC, developed by Professor Guntae Kim in September 2016.
Professor Kim and his research team have been seeking ways to improve the energy efficiency of hydrogen production, using SOEC. In the study, the research team has demonstrated the novel concept of Hybrid-SOEC based on the mixed ionic conducting electrolyte, allowing water electrolysis to occur at both hydrogen and air electrodes.
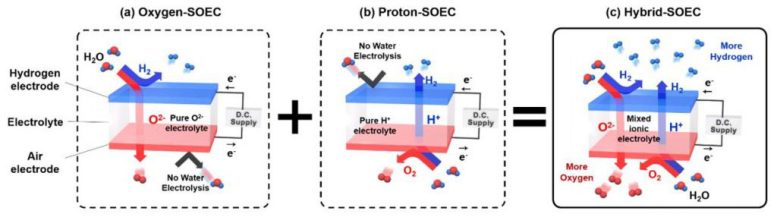
The existing SOEC electrolytes allow the transport of either only one of the hydrogen or oxygen ions to the other electrode. For cases like the SOEC electrolytes that transport oxygen ions, water electrolysis occurs at the anode, and this results in the production of hydrogen. In contrast, the SOEC electrolytes that transport hydrogen ions cause water electrolysis to occur at the cathode, and this results in the production of oxygen. Here, hydrogen travels through the electrolyte to the anode.
Theoretically, using electrolytes that transport both hydrogen and oxygen ions, allows the production of two electrolysis products, hydrogen, and oxygen, on both sides of the cell. This could improve the hydrogen production rate greatly. In the study, the research team paid attention to the control of the properties of electrolytes.
In this study, Professor Kim and his research team reported their new findings in exploring a SOEC based on a mixed-ion conductor that can transport both oxygen ion and proton at the same time, which is denoted as Hybrid-SOEC.
In comparison to other SOECs and representative water-electrolysis devices reported in the literature, the proposed system demands less electricity for hydrogen production, while exhibiting outstanding electrochemical performance with stability. Moreover, the Hybrid SOEC exhibits no observable degradation in performance for more than 60 hours of continuous operation, implying a robust system for hydrogen production.
“By controlling the driving environment of the hydrogen ion conductive electrolyte, a ‘mixed ion conductive electrolyte’ in which two ions pass can be realized,” says Junyoung Kim in the doctoral program of Energy and Chemical Engineering, the first author of the study. “In Hybrid-SOEC where this electrolyte was first introduced, water electrolysis occurred at both electrodes, which results in a significant increase in total hydrogen production.”
The layered perovskite with excellent electrochemical properties was used as the electrode of Hybrid-SOEC. By adding an excellent electrode material on mixed ionic conducting electrolyte, resulting in enhanced electrochemical performance. As a result, the corresponding yields of hydrogen produced were 1.9 L per hour at a cell voltage of 1.5 V at 700 °C. This is four times higher hydrogen production efficiency than the existing high-efficient water electrolytic cells.
Reference: “Hybrid-solid oxide electrolysis cell: A new strategy for efficient hydrogen production” by Junyoung Kim, Areum Jun, Ohhun Gwon, Seonyoung Yoo, Meilin Liu, Jeeyoung Shin, Tak-Hyoung Lim and Guntae Kim, 5 December 2017, Nano Energy.
DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.11.074








sodium is more efficient .700C. is to much for steam turbine.you weist money.
sodium is more efficient .700C. is to much for steam turbine.you waste money.