Researchers have identified a new method the immune system uses to eliminate cells that don’t have CD47 molecules marking them as “self”, with dendritic cells directly killing these CD47-lacking T cells. This discovery offers a fresh perspective for potential cancer treatments.
Researchers from Kobe University have identified an entirely new and unexpected mechanism through which the immune system eliminates cells lacking molecules that identify them as part of the self in mice. This discovery, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, may have potential implications for cancer therapy.
The immune system comprises many types of cells that work together to fight off diseases. Two important types are dendritic cells and T cells. Dendritic cells are located in strategic positions throughout the body including the gut and skin, as well as in the lymph nodes, sample their environment and present small components derived from these samples on their surface.
T cells check these samples and if they recognize them as foreign (or “non-self”), they will initiate an immune response, otherwise, they will move on. The ability to distinguish self from non-self is therefore a key characteristic of the immune system and T cells undergo very selective training, by dendritic cells, to make sure they can make that distinction.
The cells in our body display several molecules on their surface that identify them as “self” to immune cells. One of these self-identifying molecules is CD47. It was known that if T cells lack CD47, they would be efficiently eliminated by other immune cells. However, various experiments with mice lacking CD47 failed to produce an indication of the molecular mechanism of which cells were responsible for the elimination.
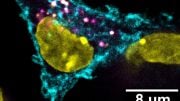
It was known that T cells are killed when they lack a surface molecule called CD47. Now, a research group at Kobe University has identified the culprit and discovered an unexpected capability of the immune system that has the potential for cancer treatment. Credit: Professor Nitta Ryo (Graduate School of Medicine, Division of Structural Medicine and Anatomy, Kobe University)
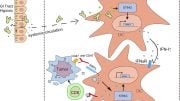
Now, the research group of Associate Professor Saito Yasuyuki, Postdoctoral fellow Komori Satomi, and Specially Appointed Professor Matozaki Takashi at Kobe University, that has been working on the molecular interaction between dendritic cells and T cells and in particular on the role of CD47 in that process, tried a novel approach. Saito explains: “We generated genetically modified mice in which only T cells lack CD47. This is quite different from the conventional approach with mice that systematically lack CD47 on all cells.” This new approach enabled them to isolate the role of CD47 on T cells from other factors that might influence the interaction.
Their results, published in the journal PNAS, clearly identified dendritic cells as those killing T cells lacking CD47. Not only does this for the first time shed light on the mechanism behind the disappearance of CD47-deficient T cells, it also reveals a completely unexpected capability of dendritic cells. “This result is totally novel because it was believed that CD47-deficient cells are engulfed by a type of immune cells called ‘macrophages’ and that dendritic cells never induce cell death in other immune cells,” says Saito. The team thus found an entirely new way in which the body identifies missing-self cells, that is, cells lacking CD47 being killed directly by dendritic cells.
This finding also suggests a new line of research. Now that this new ability of dendritic cells has been discovered, is it used on other kinds of cells, too, and can it be used therapeutically? Saito says: “Our results raise the question: do dendritic cells induce cell death in other cells that lack CD47? This question is so important because this novel mechanism can be applied to the induction of cell death by modification of CD47 on target cells, such as cancer cells.”
The group has already initiated further research projects to clarify these questions and also to better understand the mechanism behind this newly-discovered capability of dendritic cells. They have also started work to verify the potential of treating cancer based on this novel finding.
Reference: “CD47 promotes peripheral T cell survival by preventing dendritic cell–mediated T cell necroptosis” by Satomi Komori, Yasuyuki Saito, Taichi Nishimura, Datu Respatika, Hiromi Endoh, Hiroki Yoshida, Risa Sugihara, Rie Iida-Norita, Tania Afroj, Tomoko Takai, Okechi S. Oduori, Eriko Nitta, Takenori Kotani, Yoji Murata, Yoriaki Kaneko, Ryo Nitta, Hiroshi Ohnishi and Takashi Matozaki, 7 August 2023, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2304943120
The study was funded by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) Project for Accelerating Next-Generation Cancer Treatment (P-PROMOTE), the Project for Creation of Next-Generation Cancer Treatment (P-CREATE), and the JST Co-creation Opportunity Formation Support Program (COI-NEXT).


I would like to understand how quantum mechanics tech innovations could revolutionize the creation of other kinds of molecule like CD 47 for the treatment of all kind of Cancers.
So cells beat us to IFF (Identify Friend or Foe) systems by a very long time!
What about AIDS?
This research furters my theory to leave no stone unturned in all sciences, if it exists their must be a purpose behind being involved as a part of the mechanism, reaching for the purpose may take some out of the box thinking to produce answers. so many questions today are being answered do to imaginational manipulation. Ask the question to yourself how many different sciences are their that can be applied ( quantum, to standard to chemical, mechanical engineering, thermal to twisting, fluids,pressure,vacumm,charge state,optical etc.. The supreme key may be how to join them.
Great thought, and I agree that really could be the key to all of it.
It’s such an interesting time to be alive, even by those of that are not scientists!