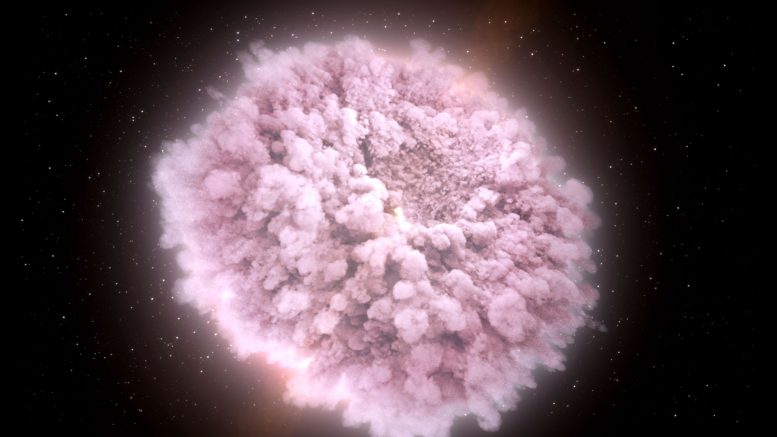
This illustration portrays the dense, heated debris cloud from colliding neutron stars, forming a kilonova—a celestial event arising from merging neutron stars or a neutron star with a black hole. Credit: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center/CI Lab
This illustration shows the hot, dense, expanding cloud of debris stripped from neutron stars just before they collided. This cloud produces a kilonova; that is an astronomical event that occurs when two neutron stars or a neutron star and a black hole merge into each other. This cloud shows the visible and infrared light. Within this neutron-rich debris, large quantities of some of the universe’s heaviest elements were forged, including hundreds of Earth masses of gold and platinum.
A kilonova (also called a macronova or r-process supernova) is a transient astronomical event that occurs in a compact binary system when two neutron stars or a neutron star and a black hole merge into each other. Kilonovae are thought to emit short gamma-ray bursts and strong electromagnetic radiation due to the radioactive decay of heavy r-process nuclei that are produced and ejected fairly isotropically during the merger process.








Be the first to comment on "Kilonova: Neutron Stars Create Gold and Platinum in Their Wake"