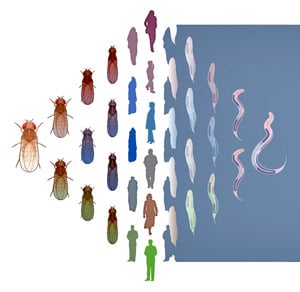
New studies reveal flies, worms, and humans share ancient patterns of gene expression. Credit: Darryl Leja, NHGRI, NIH
Several newly published studies reveal that flies, worms, and humans share ancient patterns of gene expression.
Although separated by hundreds of millions of years of evolution, flies, worms, and humans share ancient patterns of gene expression, according to a massive Yale-led analysis of genomic data.
Two related studies led by scientists at Harvard and Stanford, also published August 28 in the same issue of the journal Nature, tell a similar story: Even though humans, worms, and flies bear little obvious similarity to each other, evolution used remarkably similar molecular toolkits to shape them.
However, the same Yale lab reports in a separate paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences dramatic differences between species in genomic regions populated by pseudogenes, molecular fossils of working genes.
The human, worm, and fly genomes are all composed of the same building blocks (i.e. nucleotides) but differ greatly in size. The human genome, for instance, is more than 10 times larger than those of the worm and fly. However, the three have comparable numbers of functioning genes that code for proteins. Even more striking, note the researchers, the three share many expression programs turning genes on and off in a coordinated fashion. The gene expression patterns were so similar, in fact, that investigators were able to use them to match up the stages in worm and fly development.
“It is remarkable to find these similarities across a half billion years,’’ said Mark Gerstein, the Albert L. Williams Professor of Biomedical Informatics at Yale and senior author of one of the Nature papers. “It also illustrates how studying model organisms can help us to annotate the human genome.”
The study — spearheaded by members of the Gerstein Lab, including Joel Rozowsky, Koon-Kiu Yan, Daifeng Wang, Baikang Pei, and Arif Harmanci — looked at patterns of transcription, the process by which information encoded in DNA is transferred to RNA. The paper also reported that the control of this process by the packaging of DNA is very similar in all of the organisms. In fact, the authors were able to build a quantitative model of transcription for humans and then successfully apply it without alteration to the fly and worm.
More than 200 scientists from dozens of institutions contributed to this effort, which is collectively part of the ENCODE genomics consortium. The resulting papers published in Nature all tell similar stories of shared evolution between species — for instance, the commonalities of regulatory networks of genes and the transcription factors that control their activation.
“When we look at flies or worms, it is difficult to believe that humans have anything in common with them,” Gerstein said. “But now we can see deep similarities in them that better help us interpret the human genome.”
Stark differences emerged, however, when Gerstein’s lab looked at pseudogenes — stretches of DNA that have lost their original protein-coding gene function and are no longer under strong selective constraint, effectively representing molecular fossils. In the August 25 issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the Yale scientists reported vast differences between organisms in terms of these fossils, reflecting the divergent evolutionary histories of flies, worms, and humans.
“On one hand, we saw similarities that reflect biological necessity and, on the other hand, differences that mirrored the organism’s history,” said Cristina Sisu, postdoctoral fellow in Gerstein’s lab and the first author of the pseudogene study.
The work was funded by the National Human Genome Research Institute.
References:
“Comparative analysis of regulatory information and circuits across distant species” by Alan P. Boyle, Carlos L. Araya, Cathleen Brdlik, Philip Cayting, Chao Cheng, Yong Cheng, Kathryn Gardner, LaDeana W. Hillier, Judith Janette, Lixia Jiang, Dionna Kasper, Trupti Kawli, Pouya Kheradpour, Anshul Kundaje, Jingyi Jessica Li, Lijia Ma, Wei Niu, E. Jay Rehm, Joel Rozowsky, Matthew Slattery, Rebecca Spokony, Robert Terrell, Dionne Vafeados, Daifeng Wang, Peter Weisdepp, Yi-Chieh Wu, Dan Xie, Koon-Kiu Yan, Elise A. Feingold, Peter J. Good, Michael J. Pazin, Haiyan Huang, Peter J. Bickel, Steven E. Brenner, Valerie Reinke, Robert H. Waterston, Mark Gerstein, Kevin P. White, Manolis Kellis and Michael Snyder, 27 August 2014, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/nature13668
“Comparative analysis of metazoan chromatin organization” by Joshua W. K. Ho, Youngsook L. Jung, Tao Liu, Burak H. Alver, Soohyun Lee, Kohta Ikegami, Kyung-Ah Sohn, Aki Minoda, Michael Y. Tolstorukov, Alex Appert, Stephen C. J. Parker, Tingting Gu, Anshul Kundaje, Nicole C. Riddle, Eric Bishop, Thea A. Egelhofer, Sheng’en Shawn Hu, Artyom A. Alekseyenko, Andreas Rechtsteiner, Dalal Asker, Jason A. Belsky, Sarah K. Bowman, Q. Brent Chen, Ron A.-J. Chen, Daniel S. Day, Yan Dong, Andrea C. Dose, Xikun Duan, Charles B. Epstein, Sevinc Ercan, Elise A. Feingold, Francesco Ferrari, Jacob M. Garrigues, Nils Gehlenborg, Peter J. Good, Psalm Haseley, Daniel He, Moritz Herrmann, Michael M. Hoffman, Tess E. Jeffers, Peter V. Kharchenko, Paulina Kolasinska-Zwierz, Chitra V. Kotwaliwale, Nischay Kumar, Sasha A. Langley, Erica N. Larschan, Isabel Latorre, Maxwell W. Libbrecht, Xueqiu Lin, Richard Park, Michael J. Pazin, Hoang N. Pham, Annette Plachetka, Bo Qin, Yuri B. Schwartz, Noam Shoresh, Przemyslaw Stempor, Anne Vielle, Chengyang Wang, Christina M. Whittle, Huiling Xue, Robert E. Kingston, Ju Han Kim, Bradley E. Bernstein, Abby F. Dernburg, Vincenzo Pirrotta, Mitzi I. Kuroda, William S. Noble, Thomas D. Tullius, Manolis Kellis, David M. MacAlpine, Susan Strome, Sarah C. R. Elgin, Xiaole Shirley Liu, Jason D. Lieb, Julie Ahringer, Gary H. Karpen and Peter J. Park, 27 August 2014, Nature
DOI: 10.1038/nature13415
“Comparative analysis of pseudogenes across three phyla” by Cristina Sisu, Baikang Pei, Jing Leng, Adam Frankish, Yan Zhang, Suganthi Balasubramanian, Rachel Harte, Daifeng Wang, Michael Rutenberg-Schoenberg, Wyatt Clark, Mark Diekhans, Joel Rozowsky, Tim Hubbard, Jennifer Harrow and Mark B. Gerstein, 25 August 2014, PNAS.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1407293111







Whether it is worms, flies or even bacteria apart from humans should have the enzymes enough to digest the food they take in. A bacteria engulfs the food particle through its skin (no mouth) and after digesting to the extent required by the enzymes produced, later casts them out (exocytosis). The worms in the gut or bacteria in the gut is responsible for digesting to the extent possible the hard raw food which animals take and digest them. They are also helpful in human guts by helping digestion. Thus these worms, flies of the earlier generation had a molecular machine or encoded protein in DNA to manufacture enzymes. Whereas these primitive worms were enzyme factories, humans who takes cooked food, by evolution have lost the ability to digest any raw food and even milk in some cases. Hence our molecular factory of enzymes is whittled down by evolution to the extent required. Thus it is not surprising that protein coding DNA are common in our ancestors…. to the date in humans. Evolution is playing miracle and the copies of DNA are retained to the extent it is required and new proteins are formed as the days go by. Thank You.
I have multiple parasites that no lab or healthcare will admit and I have not confirmed why but had a very well known all over the world Parasitology Dr. and I quote “ no medical Dr. will diagnose you with a parasitic disease,I then asked him “ how can I be treated by you Dr? He said,” you won’t because first you got to get diagnosed to get to me, and before the Medical field will do that, your most likely to die first” and that was the end of that conversation.Im still suffering my symptoms are much worse, I have not worked in over a year due to the lesions and how ill I get .I did get a positive lab result for Giardia/Crypto that lasted on my Chart for a very short time before my Charts “was OMITTED AND CHANGED TO NEGATIVE “ And I say these accusations with proof before omitted because I took a screenshot of the positive/ detected results “ I can’t wrap my head around the reasoning I can only tell you how true the neglect, embarrassment and unethical our HEALTHCARE has treated me.Id like to share with you the videos and photos I’ve taken of these parasites I’ve captured with my magnifying 100 times lens, it’s truly unbelievable and very hard to believe but I promise you these photos and videos speak for themselves and will open your eyes and minds to how horrific my life has been since my first “diagnosis from an ER DR.” That was quickly dismissed thereafter in 2018 . And here I am trying to do what I can holistically because now 6 years later my life and health has declined and the number of foreign objects have definitely increased.Please don’t disrespect my intelligence or label me as psychotic but let me share with you the nitmare and distress of what living with these incredibly mind blowing,older then dinosaurs and will live on this earth when we’re all gone because I believe they can adjust to all climate changes and adapt to any environment,and that’s the observation I personally can confirm.If anyone is interested in the “REAL LIFE OF INVASION OF FOREIGN OBJECTS “? Please reach out because my photos alone tell an unbelievable and mind blowing reality.