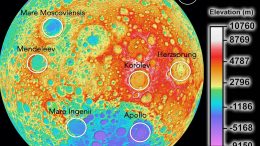
Chandra Studies Extraordinary Magnetar: Fastest Spinning and Possibly the Youngest Magnetar Known
Astronomers have recently found the fastest spinning and possibly the youngest magnetar known. This object, known as J1818.0-1607, is located about 21,000 light-years away in…