Note: There is now a newer Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Situation Report 65.
WHO Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Situation Report 64
- Four new countries/territories/areas from the South-East Asia Region (1), and Region of the Americas (3) have reported cases of COVID-19.
- WHO has delivered a new shipment of emergency medical supplies to the Islamic Republic of Iran as part of COVID-19 response measures. Details can be found on the WHO Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean here.
- The WHO WhatsApp Health Alert has now attracted 10 million users since launching Friday, and the COVID-19 Solidarity Response Fund has raised more than US$70 million, in just 10 days. The media briefing can be found here.
- WHOand FIFA launched a joint campaign to equip the football community to tackle COVID-19. This awareness campaign calls on all people around the world to follow the five key steps to stop the spread of the disease. More information can be found here.
- WHO and its partners are constantly working to strengthen the chains of essential COVID-19 supplies. As global demand rises, WHO and its partners aim to ensure assistance to areas most in need. More information can be found in Subject in Focus.
Risk Assessment
Global Level: Very High
Coronavirus Situation in Numbers
Globally
- 372,757 confirmed cases (39,827 new)
- 16,231 deaths (1,722 new)
Western Pacific Region
- 96,580 confirmed cases (943 new)
- 3,502 deaths (29 new)
European Region
- 195,511 confirmed cases (24,087 new)
- 10,189 deaths (1,447 new)
South-East Asia
- 1,990 confirmed cases (214 new)
- 65 deaths (7 new)
Eastern Mediterranean Region
- 27,215 confirmed cases (1,840 new)
- 1,877 deaths (136 new)
Regions of the Americas
- 49,444 confirmed cases (12,428 new)
- 565 deaths (100 new)
African Region
- 1305 confirmed cases (315 new)
- 26 deaths (3 new)
Subject In Focus: Strengthening Supply Chains to Create Greatest Impact
WHO and the World Food Programme (WFP) are exploring ways to work with the Pandemic Supply Chain Network (PSCN) and Logistical Emergency Teams (L.E.T.) to ensure that logistical assets are in place to support the increasing global demand for COVID-19 supplies. This is to ensure that supplies are allocated effectively and equitably in the places where they are needed the most.
WHO is also working with the World Bank to develop demand modeling from a country-based perspective. This will allow the sharing and support of technical guidance and allocation mechanisms and ensure that critical supplies are distributed with most impact.
The planning effort will support the mapping of scenarios as well as what is needed for stocks and procurement. With the engagement of the World Bank, the PSCN seeks to bring together the overview of the market’s capability to provide and distribute the necessary supplies, WHO demand forecasting and the necessary financial and political support to fight COVID-19.
Representatives from both WFP and the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA)have joined the WHO team at HQ to establish the Supply Chain Coordination Cell (SCCC). The objectives of the SCCC are to:
- Establish a COVID-19 supply chain working group to deepen inter-agency collaboration with the aim of minimizing disruptions to current humanitarian operations, while increasing the efficiency and coherence of the COVID-19 response.
- Provide a centralized voice through the collection and dissemination of information to the UN Crisis Management Team (UNCMT), other relevant forums, as well as the wider humanitarian community, to support strategic guidance, operational decision-making, and overall monitoring.
- Foster the creation of regional and country level coordination mechanisms aimed at implementing efforts, while maintaining the overall coordination of the response.
- Create a smaller joint procurement group of medical equipment buying agencies.
WHO and its partners are constantly working to strengthen the chains of essential COVID-19 supplies. As global demand rises, WHO and its partners aim to ensure that those areas most at need receive as much assistance as much as possible.
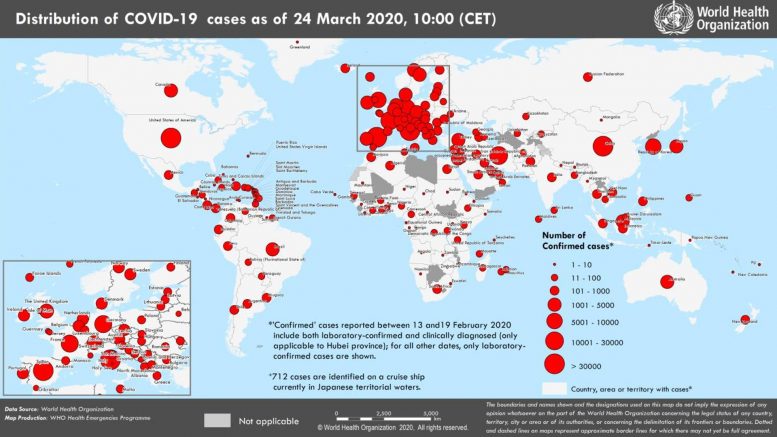
Countries, territories or areas with reported laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths, March 24, 2020
| Country/Territory/Area | Confirmed Cases |
|---|---|
| China | 81747 |
| Italy | 63927 |
| United States of America | 42164 |
| Spain | 33089 |
| Germany | 29212 |
| Iran | 23049 |
| France | 19615 |
| Republic of Korea | 9037 |
| Switzerland | 8015 |
| United Kingdom | 6654 |
| Netherlands | 4749 |
| Austria | 4486 |
| Belgium | 3743 |
| Norway | 2371 |
| Portugal | 2060 |
| Sweden | 2016 |
| Australia | 1709 |
| Brazil | 1546 |
| Turkey | 1529 |
| Malaysia | 1518 |
| Denmark | 1460 |
| Canada | 1432 |
| Israel | 1238 |
| Czech Republic | 1236 |
| Japan | 1128 |
| Ireland | 1125 |
| Pakistan | 887 |
| Luxembourg | 875 |
| Thailand | 827 |
| Ecuador | 790 |
| Poland | 749 |
| Chile | 746 |
| International (Diamond Princess Cruise Ship) | 712 |
| Finland | 700 |
| Greece | 695 |
| Iceland | 588 |
| Indonesia | 579 |
| Romania | 576 |
| Saudi Arabia | 562 |
| Singapore | 507 |
| Qatar | 501 |
| Philippines | 462 |
| Slovenia | 442 |
| Russian Federation | 438 |
| India | 434 |
| South Africa | 402 |
| Peru | 395 |
| Bahrain | 377 |
| Mexico | 370 |
| Egypt | 366 |
| Estonia | 352 |
| Panama | 345 |
| Croatia | 306 |
| Colombia | 277 |
| Lebanon | 267 |
| Argentina | 266 |
| Iraq | 266 |
| Serbia | 249 |
| Dominican Republic | 245 |
| Armenia | 235 |
| Algeria | 231 |
| Bulgaria | 201 |
| United Arab Emirates | 198 |
| Kuwait | 191 |
| Slovakia | 191 |
| Hungary | 187 |
| San Marino | 187 |
| Latvia | 180 |
| Lithuania | 179 |
| Andorra | 164 |
| Uruguay | 162 |
| Costa Rica | 158 |
| Morocco | 143 |
| North Macedonia | 136 |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 131 |
| Jordan | 127 |
| Albania | 123 |
| Vietnam | 123 |
| Faroe Islands | 118 |
| Cyprus | 116 |
| Republic of Moldova | 109 |
| Malta | 107 |
| New Zealand | 102 |
| Burkina Faso | 99 |
| Sri Lanka | 97 |
| Brunei Darussalam | 91 |
| Tunisia | 89 |
| Cambodia | 87 |
| Oman | 84 |
| Ukraine | 84 |
| Belarus | 81 |
| Senegal | 79 |
| Azerbaijan | 72 |
| Cameroon | 72 |
| Réunion | 71 |
| Venezuela | 70 |
| Georgia | 67 |
| Kazakhstan | 63 |
| Guadeloupe | 62 |
| Kosovo | 61 |
| Palestinian Territory | 59 |
| Martinique | 53 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 51 |
| Liechtenstein | 46 |
| Uzbekistan | 46 |
| Afghanistan | 42 |
| Cuba | 40 |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | 36 |
| Mauritius | 36 |
| Rwanda | 36 |
| Bangladesh | 33 |
| Puerto Rico | 31 |
| Honduras | 30 |
| Guam | 29 |
| Côte d’Ivoire | 25 |
| Bolivia | 27 |
| Ghana | 27 |
| Mayotte | 24 |
| Monaco | 23 |
| Montenegro | 22 |
| Nigeria | 22 |
| Paraguay | 22 |
| Jamaica | 19 |
| French Guiana | 20 |
| Guatemala | 20 |
| Guernsey | 20 |
| French Polynesia | 18 |
| Jersey | 18 |
| Togo | 18 |
| Barbados | 17 |
| Virgin Islands | 17 |
| Kenya | 16 |
| Kyrgyzstan | 16 |
| Gibraltar | 15 |
| Isle of Man | 13 |
| Madagascar | 13 |
| Maldives | 13 |
| United Republic of Tanzania | 12 |
| Ethiopia | 11 |
| Mongolia | 10 |
| Aruba | 9 |
| Uganda | 9 |
| New Caledonia | 8 |
| Saint Martin | 8 |
| Seychelles | 7 |
| Bermuda | 6 |
| Equatorial Guinea | 6 |
| Gabon | 6 |
| Haiti | 6 |
| Benin | 5 |
| Cayman Islands | 5 |
| Guyana | 5 |
| Bahamas | 4 |
| Central African Republic | 4 |
| Congo | 4 |
| Curaçao | 4 |
| Eswatini | 4 |
| Greenland | 4 |
| Cabo Verde | 3 |
| Djibouti | 3 |
| El Salvador | 3 |
| Fiji | 3 |
| Liberia | 3 |
| Namibia | 3 |
| Saint Barthelemy | 3 |
| Zambia | 3 |
| Angola | 2 |
| Bhutan | 2 |
| Chad | 2 |
| Guinea | 2 |
| Mauritania | 2 |
| Myanmar | 2 |
| Nepal | 2 |
| Nicaragua | 2 |
| Niger | 2 |
| Saint Lucia | 2 |
| Sint Maarten | 2 |
| Sudan | 2 |
| Suriname | 2 |
| Zimbabwe | 2 |
| Antigua and Barbuda | 1 |
| Belize | 1 |
| Dominica | 1 |
| Eritrea | 1 |
| Gambia | 1 |
| Grenada | 1 |
| Holy See | 1 |
| Montserrat | 1 |
| Mozambique | 1 |
| Papua New Guinea | 1 |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 1 |
| Somalia | 1 |
| Syrian Arab Republic | 1 |
| Timor-Leste | 1 |
| Turks and Caicos | 1 |
| Total | 372757 |
Recommendations and Advice for the Public
If you are not in an area where COVID-19 is spreading or have not traveled from an area where COVID-19 is spreading or have not been in contact with an infected patient, your risk of infection is low. It is understandable that you may feel anxious about the outbreak. Get the facts from reliable sources to help you accurately determine your risks so that you can take reasonable precautions (see Frequently Asked Questions). Seek guidance from WHO, your healthcare provider, your national public health authority or your employer for accurate information on COVID-19 and whether COVID-19 is circulating where you live. It is important to be informed of the situation and take appropriate measures to protect yourself and your family (see Protection measures for everyone).
If you are in an area where there are cases of COVID-19 you need to take the risk of infection seriously. Follow the advice of WHO and guidance issued by national and local health authorities. For most people, COVID-19 infection will cause mild illness however, it can make some people very ill and, in some people, it can be fatal. Older people, and those with pre-existing medical conditions (such as cardiovascular disease, chronic respiratory disease or diabetes) are at risk for severe disease (See Protection measures for persons who are in or have recently visited (past 14 days) areas where COVID-19 is spreading).
Case Definitions
WHO periodically updates the Global Surveillance for human infection with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) document which includes case definitions.
For easy reference, case definitions are included below.
Suspect case
A. A patient with acute respiratory illness (fever and at least one sign/symptom of respiratory disease, e.g., cough, shortness of breath), AND a history of travel to or residence in a location reporting community transmission of COVID-19 disease during the 14 days prior to symptom onset.
OR
B. A patient with any acute respiratory illness AND having been in contact with a confirmed or probable COVID-19 case (see definition of contact) in the last 14 days prior to symptom onset;
OR
C. A patient with severe acute respiratory illness (fever and at least one sign/symptom of respiratory disease, e.g., cough, shortness of breath; AND requiring hospitalization) AND in the absence of an alternative diagnosis that fully explains the clinical presentation.
Probable case
A. A suspect case for whom testing for the COVID-19 virus is inconclusive.
a. Inconclusive being the result of the test reported by the laboratory.
OR
B. A suspect case for whom testing could not be performed for any reason.
Confirmed case
A person with laboratory confirmation of COVID-19 infection, irrespective of clinical signs and symptoms.
- Technical guidance for laboratory testing can be found here.
Definition of contact
A contact is a person who experienced any one of the following exposures during the 2 days before and the 14 days after the onset of symptoms of a probable or confirmed case:
- Face-to-face contact with a probable or confirmed case within 1 meter and for more than 15 minutes;
- Direct physical contact with a probable or confirmed case;
- Direct care for a patient with probable or confirmed COVID-19 disease without using proper personal protective equipment; OR
- Other situations as indicated by local risk assessments.
Note: for confirmed asymptomatic cases, the period of contact is measured as the 2 days before through the 14 days after the date on which the sample was taken which led to confirmation.









Be the first to comment on "COVID-19 World Map: 372,757 Confirmed Cases; 190 Countries; 16,231 Deaths"