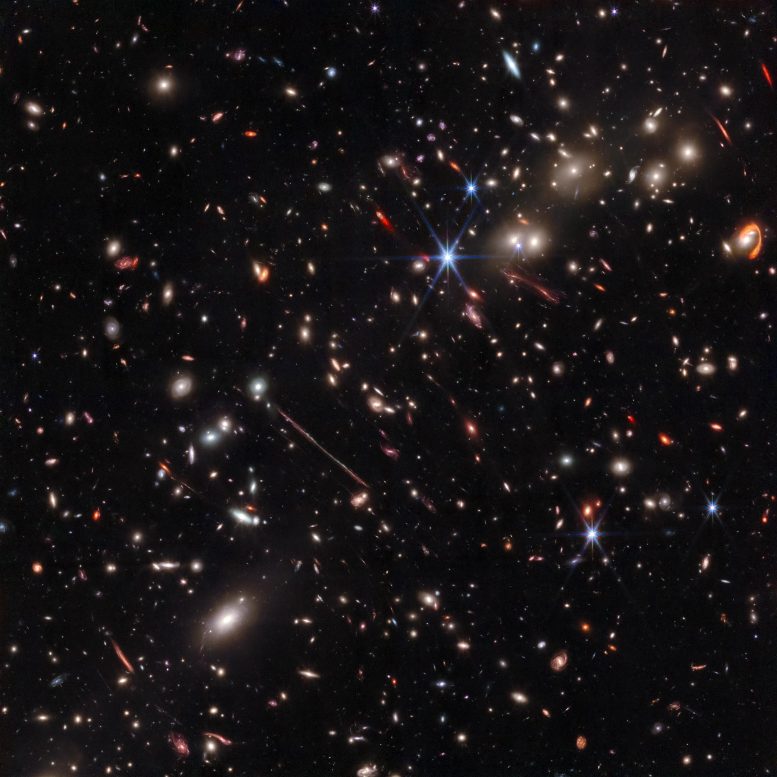

Webb’s infrared image of the galaxy cluster El Gordo (“the Fat One”) reveals hundreds of galaxies, some never before seen at this level of detail. El Gordo acts as a gravitational lens, distorting and magnifying the light from distant background galaxies. Two of the most prominent features in the image include the Thin One, located just below and left of the image center, and the Fishhook, a red swoosh at upper right. Both are lensed background galaxies. Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, Jose M. Diego (IFCA), Brenda Frye (University of Arizona), Patrick Kamieneski (ASU), Tim Carleton (ASU), Rogier Windhorst (ASU)
A new image reveals galaxy groups, smudges, and dusty distant objects.
The Fishhook. The Thin One. These are just two of the striking targets revealed in new detail by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. In July 2022 Webb observed El Gordo, a galaxy cluster that existed 6.2 billion years after the big bang. It was selected as the most massive galaxy cluster known at that time in cosmic history.
Galaxy clusters are the heavyweights of astronomy. They have the power to bend and magnify light from more distant objects, a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing that was predicted by Albert Einstein more than 100 years ago. Webb’s infrared image of El Gordo displays a variety of unusual, distorted background galaxies. It also has fueled several new scientific discoveries.
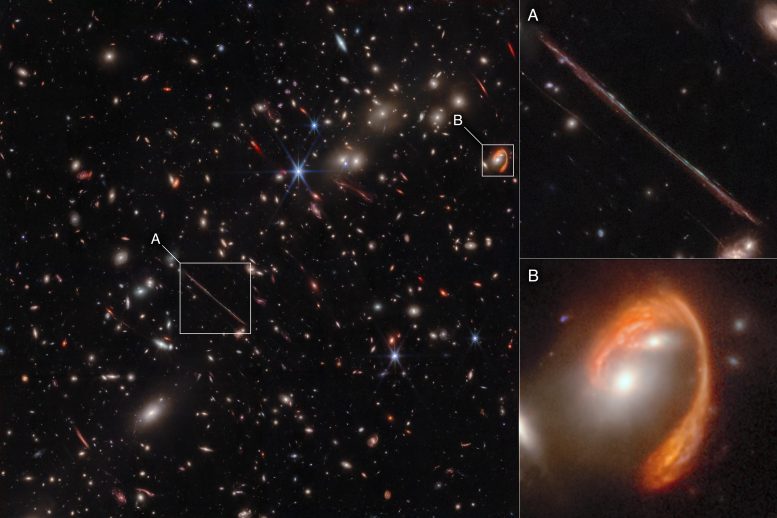
Webb’s infrared image of the galaxy cluster El Gordo (“the Fat One”) reveals hundreds of galaxies, some never before seen at this level of detail. El Gordo acts as a gravitational lens, distorting and magnifying the light from distant background galaxies. Two of the most prominent features in the image include the Thin One, highlighted in box A, and the Fishhook, a red swoosh highlighted in box B. Both are lensed background galaxies. The insets at right show zoomed-in views of both objects. Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, Jose M. Diego (IFCA), Brenda Frye (University of Arizona), Patrick Kamieneski (ASU), Tim Carleton (ASU), Rogier Windhorst (ASU), Alyssa Pagan (STScI), Jake Summers (ASU), Jordan C. J. D’Silva (UWA), Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI), Aaron Robotham (UWA), Rogier Windhorst (ASU)
Webb Space Telescope Spotlights Gravitational Arcs in ‘El Gordo’ Galaxy Cluster
A recently captured image of the galaxy cluster, famously known as “El Gordo,” is exposing never-before-seen distant and dusty celestial objects, thereby offering new scientific revelations. The infrared image, snapped by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, showcases a plethora of unique, twisted background galaxies that were only partially hinted at in previous Hubble Space Telescope images.
El Gordo is a cluster of hundreds of galaxies that existed when the universe was 6.2 billion years old, making it a “cosmic teenager.” It’s the most massive cluster known to exist at that time. (“El Gordo” is Spanish for the “Fat One.”)
Gravitational Lensing and El Gordo
El Gordo was chosen as the object of study due to its characteristic function as a natural, cosmic magnifying glass. This is made possible through a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing, where the potent gravity of El Gordo warps and distorts the light of the objects located behind it, similar to how an eyeglass lens functions.
“Lensing by El Gordo boosts the brightness and magnifies the sizes of distant galaxies. This lensing effect provides a unique window into the distant universe,” said Brenda Frye of the University of Arizona. Frye is co-lead of the PEARLS-Clusters branch of the Prime Extragalactic Areas for Reionization and Lensing Science (PEARLS) team and lead author of one of four papers[1] analyzing the El Gordo observations.
In July 2022, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope observed El Gordo, a galaxy cluster that existed 6.2 billion years after the big bang. It was selected as the most massive galaxy cluster known at that time in cosmic history. The resulting image reveals a variety of gravitationally lensed galaxies, including striking objects nicknamed the Fishhook and the Thin One. Come with us on a video tour of this new infrared image from Webb.
The Fishhook
Within the image of El Gordo, one of the most striking features is a bright arc represented in red at upper right. Nicknamed “El Anzuelo” (The Fishhook) by one of Frye’s students, the light from this galaxy took 10.6 billion years to reach Earth. Its distinctive red color is due to a combination of reddening from dust within the galaxy itself and cosmological redshift due to its extreme distance.
By correcting for the distortions created by lensing, the team was able to determine that the background galaxy is disk-shaped but only 26,000 light-years in diameter – about one-fourth the size of the Milky Way. They also were able to study the galaxy’s star formation history, finding that star formation was already rapidly declining in the galaxy’s center, a process known as quenching.
“We were able to carefully dissect the shroud of dust that envelops the galaxy center where stars are actively forming,” said Patrick Kamieneski of Arizona State University, lead author on a second paper.[2] “Now, with Webb, we can peer through this thick curtain of dust with ease, allowing us to see firsthand the assembly of galaxies from the inside out.”

This is an image of the El Gordo galaxy cluster with compass arrows, scale bar and color key. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east on the sky (as seen from below) is flipped relative to direction arrows on a map of the ground (as seen from above).
This image shows invisible near-infrared wavelengths of light that have been translated into visible-light colors. The color key shows which NIRCam filters were used when collecting the light. The color of each filter name is the visible light color used to represent the infrared light that passes through that filter. Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, Jose M. Diego (IFCA), Brenda Frye (University of Arizona), Patrick Kamieneski (ASU), Tim Carleton (ASU), Rogier Windhorst (ASU), Alyssa Pagan (STScI), Jake Summers (ASU), Jordan C. J. D’Silva (UWA), Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI), Aaron Robotham (UWA), Rogier Windhorst (ASU)
The Thin One
Another prominent feature in the Webb image is a long, pencil-thin line at left of center. Known as “La Flaca” (the Thin One), it is another lensed background galaxy whose light also took nearly 11 billion years to reach Earth.
Not far from La Flaca is another lensed galaxy. When the researchers examined that galaxy closely, they found three images of a single red giant star that they nicknamed Quyllur, which is the Quechua term for star.
Previously, Hubble has found other lensed stars (such as Earendel), but they were all blue supergiants. Quyllur is the first individual red giant star observed beyond 1 billion light-years from Earth. Such stars at high redshift are only detectable using the infrared filters and sensitivity of Webb.
“It’s almost impossible to see lensed red giant stars unless you go into the infrared. This is the first one we’ve found with Webb, but we expect there will be many more to come,” said Jose Diego of the Instituto de Física de Cantabria in Spain, lead author of a third paper[3] on El Gordo.
Galaxy Group and Smudges
Other objects within the Webb image, while less prominent, are equally interesting scientifically. For example, Frye and her team (which includes nine students from high school to graduate students) identified five multiply lensed galaxies that appear to be a baby galaxy cluster forming about 12.1 billion years ago. There are another dozen candidate galaxies that may also be part of this distant cluster.
“While additional data are required to confirm that there are 17 members of this cluster, we may be witnessing a new galaxy cluster forming right before our eyes, just over a billion years after the big bang,” said Frye.
A final paper[4] examines very faint, smudge-like galaxies known as ultra-diffuse galaxies. As their name suggests, these objects, which are scattered throughout the El Gordo cluster, have their stars widely spread out across space. The team identified some of the most distant ultra-diffuse galaxies ever observed, whose light traveled 7.2 billion years to reach us.
“We examined whether the properties of these galaxies are any different than the ultra-diffuse galaxies we see in the local universe, and we do actually see some differences. In particular, they are bluer, younger, more extended, and more evenly distributed throughout the cluster. This suggests that living in the cluster environment for the past 6 billion years has had a significant effect on these galaxies,” explained Timothy Carleton of Arizona State University, lead author on the fourth paper.
“Gravitational lensing was predicted by Albert Einstein more than 100 years ago. In the El Gordo cluster, we see the power of gravitational lensing in action,” concluded Rogier Windhorst of Arizona State University, principal investigator of the PEARLS program. “The PEARLS images of El Gordo are out-of-this-world beautiful. And, they have shown us how Webb can unlock Einstein’s treasure chest.”
The paper by Frye et al. has been published in The Astrophysical Journal. The paper by Kamieneski et al. has been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. The paper by Diego et al. has been published in Astronomy & Astrophysics. The paper by Carleton et al. has been published in The Astrophysical Journal.
References:
- “The JWST PEARLS View of the El Gordo Galaxy Cluster and of the Structure It Magnifies” by Brenda L. Frye, Massimo Pascale, Nicholas Foo, Reagen Leimbach, Nikhil Garuda, Paulina Soto Robles, Jake Summers, Carlos Diaz, Patrick Kamieneski, Lukas J. Furtak, Seth H. Cohen, Jose Diego, Benjamin Beauchesne, Rogier A. Windhorst, S. P. Willner, Anton M. Koekemoer, Adi Zitrin, Gabriel Caminha, Karina I. Caputi, Dan Coe, Christopher J. Conselice, Liang Dai, Hervé Dole, Simon P. Driver, Norman A. Grogin, Kevin Harrington, Rolf A. Jansen, Jean-Paul Kneib, Matt Lehnert, James Lowenthal, Madeline A. Marshall, Felipe Menanteau, Belén Alcalde Pampliega, Nor Pirzkal, Mari Polletta, Johan Richard, Aaron Robotham, Russell E. Ryan Jr., Michael J. Rutkowski, Christóbal Sifón, Scott Tompkins, Daniel Wang, Haojing Yan and Min S. Yun, 19 July 2023, The Astrophysical Journal.
DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/acd929 - “Are JWST/NIRCam color gradients in the lensed z=2.3 dusty star-forming galaxy El Anzuelo due to central dust attenuation or inside-out galaxy growth?” by Patrick S. Kamieneski, Brenda L. Frye, Massimo Pascale, Seth H. Cohen, Rogier A. Windhorst, Rolf A. Jansen, Min S. Yun, Cheng Cheng, Jake S. Summers, Timothy Carleton, Kevin C. Harrington, Jose M. Diego, Haojing Yan, Anton M. Koekemoer, Christopher N. A. Willmer, Andreea Petric, Lukas J. Furtak, Nicholas Foo, Christopher J. Conselice, Dan Coe, Simon P. Driver, Norman A. Grogin, Madeline A. Marshall, Nor Pirzkal, Aaron S. G. Robotham, Russell E. Ryan Jr. and Scott Tompkins, Accepted, The Astrophysical Journal.
arXiv:2303.05054v2 - “JWST’s PEARLS: A new lens model for ACT-CL J0102−4915, “El Gordo,” and the first red supergiant star at cosmological distances discovered by JWST” by J. M. Diego, A. K. Meena, N. J. Adams, T. Broadhurst, L. Dai, D. Coe, B. Frye, P. Kelly, A. M. Koekemoer, M. Pascale, S. P. Willner, E. Zackrisson, A. Zitrin, R. A. Windhorst, S. H. Cohen, R. A. Jansen, J. Summers, S. Tompkins, C. J. Conselice, S. P. Driver, H. Yan, N. Grogin, M. A. Marshall, N. Pirzkal, A. Robotham, R. E. Ryan Jr., C. N. A. Willmer, L. D. Bradley, G. Caminha, K. Caputi, T. Carleton and P. Kamieneski, 23 March 2023, Astronomy & Astrophysics.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202245238 - “PEARLS: Low Stellar Density Galaxies in the El Gordo Cluster Observed with JWST” by Timothy Carleton, Seth H. Cohen, Brenda L. Frye, Alex Pigarelli, Jiashuo Zhang, Rogier A. Windhorst, Jose M. Diego, Christopher J. Conselice, Cheng Cheng, Simon P. Driver, Nicholas Foo, Rachana A. Bhatawdekar, Patrick Kamieneski, Rolf A. Jansen, Haojing Yan, Jake Summers, Aaron S. G. Robotham, Christopher N. A. Willmer, Anton M. Koekemoer, Scott Tompkins, Dan Coe, Norman A. Grogin, Madeline A. Marshall, Mario Nonino, Nor Pirzka and Russell E. Ryan Jr., 4 August 2023, The Astrophysical Journal.
DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ace343
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency.








Be the first to comment on "Unlocking Einstein’s Treasure Chest: Webb’s Intriguing Insights Into the “El Gordo” Galaxy Cluster"