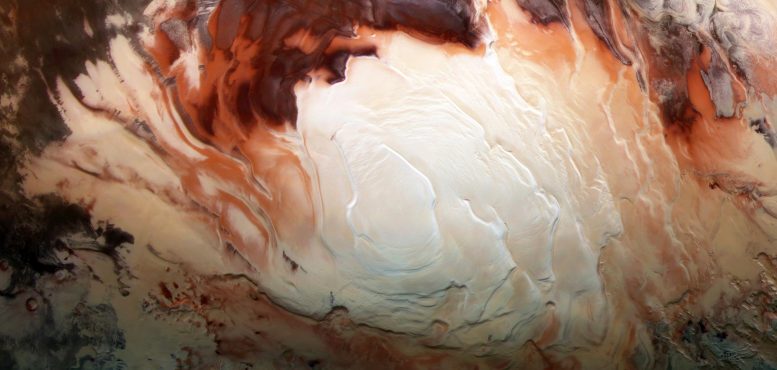
The bright white region of this image shows the icy cap that covers Mars’ south pole, composed of frozen water and frozen carbon dioxide. ESA’s Mars Express imaged this area of Mars on December 17, 2012, in infrared, green and blue light, using its High Resolution Stereo Camera. Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin/Bill Dunford
Is there water on Mars? There sure is! It’s not exactly like water on Earth but Martian H20 can tell us a lot about the planet’s distant past while potentially aiding explorers in the future. Some of the water is even trapped inside rocks! Hear from Mars scientist Eva Scheller who helped make that discovery using NASA data.
The short answer is yes. Now, we have to think about, how do we actually define water? It’s not quite like on Earth, but it’s definitely there. Water is a molecule that has one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms. The ice on Mars is a little bit different than on Earth.
On Earth, usually the ice is just, you know, water ice. But on Mars, it’s actually water ice and CO2 ice mixed with each other. On Mars, it’s just so cold that it gets frozen, so you actually have those mixed together both at the poles and underneath the surface as well. We even have water in the atmosphere as a water vapor. It’s a very small amount, but it’s there.
We also have water inside of rocks. So, you can think about rocks as sort of a stack of layers and sometimes there’s water trapped in between those layers. We’ve actually measured this with a lot of the different missions from NASA and that’s actually what I study. And the last state of potential state of water is, do we have liquid water on Mars? The answer is we haven’t really observed it. We do see these dark streaks on some hillsides that we call recurring slope lineae.
One idea is that these slope lineae could be formed by the flow of liquid water. But there’s also other ideas where you actually don’t need liquid water to explain the formation of these dark streaks. Maybe they could form through sand flow or that kind of thing.
So, is there water on Mars? Not quite like the oceans we know on Earth, but it’s definitely there.
We Asked a NASA Expert Video Series
- Why is Venus Called Earth’s Evil Twin?
- Is NASA Really Crashing a Spacecraft Into an Asteroid?
- Is NASA Aware of Any Earth-Threatening Asteroids?
- When Was the Last Time an Asteroid Hit Earth?
- How Did Perseverance Mars Rover Pick Its Landing Spot?
- What if an Asteroid Was Going To Hit Earth?
- Did Mars Ever Look Like Earth?
- What Are Lagrange Points?
- What Are the Trojan Asteroids?
- Is There Oxygen on Mars?
- Does NASA Know About All the Asteroids?
- Do Aliens Exist?
- Is There Weather on Mars?
- Will an Asteroid Ever Hit Earth?
- Is Mars Habitable?
- Could Microbes Survive a Trip to Mars?







If there is water they can create hydrogen and oxygen fuel to aid return trips to earth.
Beaucoup d’effort ONG été faits et nous savons désormais ce qu’est Mars. Elle avait même plus ce qu’a la terre comme vie. le Rover nous le confirme par les très anciens sous bâtiments d’habitations qu’il présente depuis son atterrissage sur cette planète. Ma préoccupations : pourquoi nous ne cherchons pas à savoir un peu la cause dont l’effet aurait éradiqué toutes vie sur cette planète ? Même les quelques H2o dont vous parlez, depuis leur cachette, sont menacés par ces volumineux dioxyde de carbone envahisseurs qui auraient intoxiqués ce monde.
Then how about CN? They did worse in 2021?