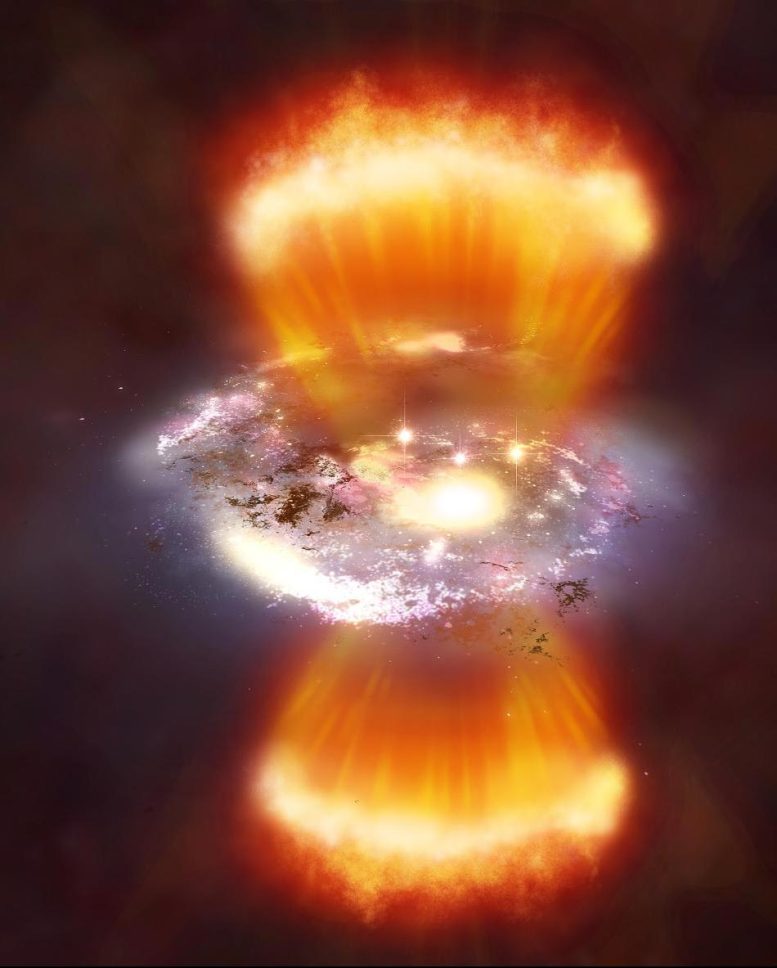

Artist’s depiction of Lyman Alpha Blob
In extragalactic astronomy, a Lyman-alpha blob (LAB) is a huge concentration of gas emitting the Lyman-alpha emission line, a spectral line of hydrogen, or more generally of one-electron ions, in the Lyman series. Lyman-alpha blobs are some of the largest known individual objects in the observable universe.
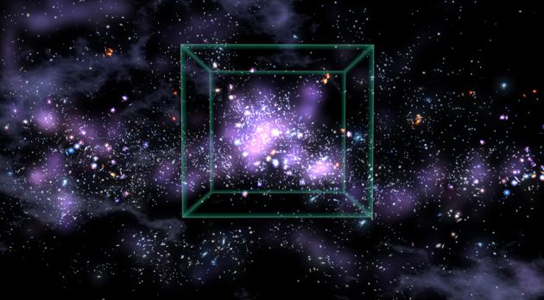
Some of these gaseous structures are more than 400,000 light-years across and have only been found in the high-redshift universe, which is due to the ultraviolet nature of the Lyman-alpha emission line.

Some of the most famous Lyman-alpha blobs were discovered in 2000 by Steidel, Mastuda and their colleagues, using the Subaru Telescope of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan. Since then, over thirty new LABs have been found, but most of these are smaller than the ones which were found originally. Together, these LABs form a structure that is more than 200 million light-years in extent and it’s currently unknown whether LABs trace overdensities of galaxies in the high-redshift universe, like high-redshift radio galaxies, which also have extended Lyman-alpha halos.
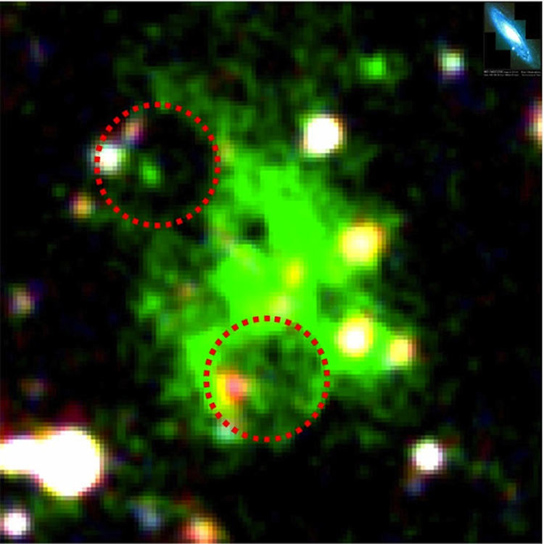
It’s also unknown which mechanism produces the Lyman-alpha emission line or how the LABs are connected to the galaxies that surround them. Further study of LABs might reveal clues on how exactly galaxies are formed.
The Himiko Lyman-alpha blob is one of the most massive objects ever discovered in the early universe, and it’s 12.9 billion light-years from Earth. It’s 55,000 light-years across, which is half of the diameter of the Milky Way, but it is said to hold more than 10 times as much mass as the next largest (known) early universe, roughly equivalent to 40 billion M☉(solar masses). This makes it the most massive object in the known universe.








10 times as much mass as the next largest universe, roughly equivalent to 40 billion M☉
misprint, I assume. you mean next largest LAB ?
The information came from Wikipedia and the cited work bellow.
“…. but is said to “hold more than 10 times as much mass as the next largest object found in the early universe, or roughly the equivalent mass of 40 billion suns”, making it the most massive object in the known universe.[1]”
Citations
^ a b c d Hsu, Jeremy (2009-04-22). “Giant Mystery Blob Discovered Near Dawn of Time“. SPACE.com. Retrieved 2009-04-24.
As James so nicely pointed out, thanks to a citation, no it’s not a misprint. It comes directly from a citation. Thanks.
Range/Staff – The citation must have been corrected, because it clearly states “the next largest object in the —-early—– universe”.
It’s a typo on the scitechdaily’s part. We have no idea what the mass of the “next largest universe” is……..